Looker
There are 2 sources that provide integration with Looker
| Source Module | Documentation |
| This plugin extracts the following:
note To get complete Looker metadata integration (including Looker views and lineage to the underlying warehouse tables), you must ALSO use the |
| This plugin extracts the following:
note To get complete Looker metadata integration (including Looker dashboards and charts and lineage to the underlying Looker views, you must ALSO use the |
Module looker
Important Capabilities
| Capability | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Containers | ✅ | Enabled by default. Supported for types - LookML Model, Folder. |
| Column-level Lineage | ✅ | Enabled by default, configured using extract_column_level_lineage. |
| Dataset Usage | ✅ | Enabled by default, configured using extract_usage_history. |
| Descriptions | ✅ | Enabled by default. |
| Detect Deleted Entities | ✅ | Enabled by default via stateful ingestion. |
| Extract Ownership | ✅ | Enabled by default, configured using extract_owners. |
| Platform Instance | ✅ | Use the platform_instance field. |
| Table-Level Lineage | ✅ | Supported by default. |
| Test Connection | ✅ | Enabled by default. |
This plugin extracts the following:
- Looker dashboards, dashboard elements (charts) and explores
- Names, descriptions, URLs, chart types, input explores for the charts
- Schemas and input views for explores
- Owners of dashboards
To get complete Looker metadata integration (including Looker views and lineage to the underlying warehouse tables), you must ALSO use the lookml module.
Prerequisites
Set up the right permissions
You need to provide the following permissions for ingestion to work correctly.
access_data
explore
manage_models
see_datagroups
see_lookml
see_lookml_dashboards
see_looks
see_pdts
see_queries
see_schedules
see_sql
see_system_activity
see_user_dashboards
see_users
Here is an example permission set after configuration.

Get an API key
You need to get an API key for the account with the above privileges to perform ingestion. See the Looker authentication docs for the steps to create a client ID and secret.
Ingestion through UI
The following video shows you how to get started with ingesting Looker metadata through the UI.
You will need to run lookml ingestion through the CLI after you have ingested Looker metadata through the UI. Otherwise you will not be able to see Looker Views and their lineage to your warehouse tables.
CLI based Ingestion
Starter Recipe
Check out the following recipe to get started with ingestion! See below for full configuration options.
For general pointers on writing and running a recipe, see our main recipe guide.
source:
type: "looker"
config:
# Coordinates
base_url: "https://<company>.cloud.looker.com"
# Credentials
client_id: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET}
# Liquid variables
# liquid_variables:
# _user_attributes:
# looker_env: "dev"
# dev_database_prefix: "employee"
# dev_schema_prefix: "public"
# dw_eff_dt_date:
# _is_selected: true
# source_region: "ap-south-1"
# db: "test-db"
# LookML Constants
# lookml_constants:
# star_award_winner_year: "public.winner_2025"
# sink configs
Config Details
- Options
- Schema
Note that a . is used to denote nested fields in the YAML recipe.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
base_url ✅ string | Url to your Looker instance: https://company.looker.com:19999 or https://looker.company.com, or similar. Used for making API calls to Looker and constructing clickable dashboard and chart urls. |
client_id ✅ string | Looker API client id. |
client_secret ✅ string(password) | Looker API client secret. |
emit_used_explores_only boolean | When enabled, only explores that are used by a Dashboard/Look will be ingested. Default: True |
external_base_url One of string, null | Optional URL to use when constructing external URLs to Looker if the base_url is not the correct one to use. For example, https://looker-public.company.com. If not provided, the external base URL will default to base_url. Default: None |
extract_column_level_lineage boolean | When enabled, extracts column-level lineage from Views and Explores Default: True |
extract_embed_urls boolean | Produce URLs used to render Looker Explores as Previews inside of DataHub UI. Embeds must be enabled inside of Looker to use this feature. Default: True |
extract_independent_looks boolean | Extract looks which are not part of any Dashboard. To enable this flag the stateful_ingestion should also be enabled. Default: False |
extract_owners boolean | When enabled, extracts ownership from Looker directly. When disabled, ownership is left empty for dashboards and charts. Default: True |
extract_usage_history boolean | Whether to ingest usage statistics for dashboards. Setting this to True will query looker system activity explores to fetch historical dashboard usage. Default: True |
extract_usage_history_for_interval string | Used only if extract_usage_history is set to True. Interval to extract looker dashboard usage history for. See https://docs.looker.com/reference/filter-expressions#date_and_time. Default: 30 days |
include_deleted boolean | Whether to include deleted dashboards and looks. Default: False |
include_platform_instance_in_urns boolean | When enabled, platform instance will be added in dashboard and chart urn. Default: False |
max_retries integer | Number of retries for Looker API calls Default: 3 |
max_threads integer | Max parallelism for Looker API calls. Defaults to cpuCount or 40 |
platform_instance One of string, null | The instance of the platform that all assets produced by this recipe belong to. This should be unique within the platform. See https://docs.datahub.com/docs/platform-instances/ for more details. Default: None |
skip_personal_folders boolean | Whether to skip ingestion of dashboards in personal folders. Setting this to True will only ingest dashboards in the Shared folder space. Default: False |
strip_user_ids_from_email boolean | When enabled, converts Looker user emails of the form name@domain.com to urn:li:corpuser:name when assigning ownership Default: False |
tag_measures_and_dimensions boolean | When enabled, attaches tags to measures, dimensions and dimension groups to make them more discoverable. When disabled, adds this information to the description of the column. Default: True |
env string | The environment that all assets produced by this connector belong to Default: PROD |
chart_pattern AllowDenyPattern | A class to store allow deny regexes |
chart_pattern.ignoreCase One of boolean, null | Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching. Default: True |
dashboard_pattern AllowDenyPattern | A class to store allow deny regexes |
dashboard_pattern.ignoreCase One of boolean, null | Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching. Default: True |
explore_browse_pattern LookerNamingPattern | |
explore_browse_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
explore_naming_pattern LookerNamingPattern | |
explore_naming_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
folder_path_pattern AllowDenyPattern | A class to store allow deny regexes |
folder_path_pattern.ignoreCase One of boolean, null | Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching. Default: True |
transport_options One of TransportOptionsConfig, null | Populates the TransportOptions struct for looker client Default: None |
transport_options.headers ❓ map(str,string) | |
transport_options.timeout ❓ integer | |
view_browse_pattern LookerViewNamingPattern | |
view_browse_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
view_naming_pattern LookerViewNamingPattern | |
view_naming_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
stateful_ingestion One of StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig, null | Default: None |
stateful_ingestion.enabled boolean | Whether or not to enable stateful ingest. Default: True if a pipeline_name is set and either a datahub-rest sink or datahub_api is specified, otherwise False Default: False |
stateful_ingestion.fail_safe_threshold number | Prevents large amount of soft deletes & the state from committing from accidental changes to the source configuration if the relative change percent in entities compared to the previous state is above the 'fail_safe_threshold'. Default: 75.0 |
stateful_ingestion.remove_stale_metadata boolean | Soft-deletes the entities present in the last successful run but missing in the current run with stateful_ingestion enabled. Default: True |
The JSONSchema for this configuration is inlined below.
{
"$defs": {
"AllowDenyPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "A class to store allow deny regexes",
"properties": {
"allow": {
"default": [
".*"
],
"description": "List of regex patterns to include in ingestion",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Allow",
"type": "array"
},
"deny": {
"default": [],
"description": "List of regex patterns to exclude from ingestion.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Deny",
"type": "array"
},
"ignoreCase": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "boolean"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": true,
"description": "Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching.",
"title": "Ignorecase"
}
},
"title": "AllowDenyPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerNamingPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"pattern": {
"title": "Pattern",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"pattern"
],
"title": "LookerNamingPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerViewNamingPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"pattern": {
"title": "Pattern",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"pattern"
],
"title": "LookerViewNamingPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Base specialized config for Stateful Ingestion with stale metadata removal capability.",
"properties": {
"enabled": {
"default": false,
"description": "Whether or not to enable stateful ingest. Default: True if a pipeline_name is set and either a datahub-rest sink or `datahub_api` is specified, otherwise False",
"title": "Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"remove_stale_metadata": {
"default": true,
"description": "Soft-deletes the entities present in the last successful run but missing in the current run with stateful_ingestion enabled.",
"title": "Remove Stale Metadata",
"type": "boolean"
},
"fail_safe_threshold": {
"default": 75.0,
"description": "Prevents large amount of soft deletes & the state from committing from accidental changes to the source configuration if the relative change percent in entities compared to the previous state is above the 'fail_safe_threshold'.",
"maximum": 100.0,
"minimum": 0.0,
"title": "Fail Safe Threshold",
"type": "number"
}
},
"title": "StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig",
"type": "object"
},
"TransportOptionsConfig": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"timeout": {
"title": "Timeout",
"type": "integer"
},
"headers": {
"additionalProperties": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Headers",
"type": "object"
}
},
"required": [
"timeout",
"headers"
],
"title": "TransportOptionsConfig",
"type": "object"
}
},
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"platform_instance": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "The instance of the platform that all assets produced by this recipe belong to. This should be unique within the platform. See https://docs.datahub.com/docs/platform-instances/ for more details.",
"title": "Platform Instance"
},
"env": {
"default": "PROD",
"description": "The environment that all assets produced by this connector belong to",
"title": "Env",
"type": "string"
},
"stateful_ingestion": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": ""
},
"explore_naming_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "{model}.explore.{name}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing dataset names to explores. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name']"
},
"explore_browse_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "/Explore/{model}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing browse paths to explores. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name']"
},
"view_naming_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerViewNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "{project}.view.{name}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing dataset names to views. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name', 'file_path', 'folder_path']"
},
"view_browse_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerViewNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "/Develop/{project}/{folder_path}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing browse paths to views. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name', 'file_path', 'folder_path']"
},
"tag_measures_and_dimensions": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, attaches tags to measures, dimensions and dimension groups to make them more discoverable. When disabled, adds this information to the description of the column.",
"title": "Tag Measures And Dimensions",
"type": "boolean"
},
"extract_column_level_lineage": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, extracts column-level lineage from Views and Explores",
"title": "Extract Column Level Lineage",
"type": "boolean"
},
"client_id": {
"description": "Looker API client id.",
"title": "Client Id",
"type": "string"
},
"client_secret": {
"description": "Looker API client secret.",
"format": "password",
"title": "Client Secret",
"type": "string",
"writeOnly": true
},
"base_url": {
"description": "Url to your Looker instance: `https://company.looker.com:19999` or `https://looker.company.com`, or similar. Used for making API calls to Looker and constructing clickable dashboard and chart urls.",
"title": "Base Url",
"type": "string"
},
"transport_options": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/TransportOptionsConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Populates the [TransportOptions](https://github.com/looker-open-source/sdk-codegen/blob/94d6047a0d52912ac082eb91616c1e7c379ab262/python/looker_sdk/rtl/transport.py#L70) struct for looker client"
},
"max_retries": {
"default": 3,
"description": "Number of retries for Looker API calls",
"title": "Max Retries",
"type": "integer"
},
"dashboard_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/AllowDenyPattern",
"default": {
"allow": [
".*"
],
"deny": [],
"ignoreCase": true
},
"description": "Patterns for selecting dashboard ids that are to be included"
},
"chart_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/AllowDenyPattern",
"default": {
"allow": [
".*"
],
"deny": [],
"ignoreCase": true
},
"description": "Patterns for selecting chart ids that are to be included"
},
"include_deleted": {
"default": false,
"description": "Whether to include deleted dashboards and looks.",
"title": "Include Deleted",
"type": "boolean"
},
"extract_owners": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, extracts ownership from Looker directly. When disabled, ownership is left empty for dashboards and charts.",
"title": "Extract Owners",
"type": "boolean"
},
"strip_user_ids_from_email": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, converts Looker user emails of the form name@domain.com to urn:li:corpuser:name when assigning ownership",
"title": "Strip User Ids From Email",
"type": "boolean"
},
"skip_personal_folders": {
"default": false,
"description": "Whether to skip ingestion of dashboards in personal folders. Setting this to True will only ingest dashboards in the Shared folder space.",
"title": "Skip Personal Folders",
"type": "boolean"
},
"max_threads": {
"description": "Max parallelism for Looker API calls. Defaults to cpuCount or 40",
"title": "Max Threads",
"type": "integer"
},
"external_base_url": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Optional URL to use when constructing external URLs to Looker if the `base_url` is not the correct one to use. For example, `https://looker-public.company.com`. If not provided, the external base URL will default to `base_url`.",
"title": "External Base Url"
},
"extract_usage_history": {
"default": true,
"description": "Whether to ingest usage statistics for dashboards. Setting this to True will query looker system activity explores to fetch historical dashboard usage.",
"title": "Extract Usage History",
"type": "boolean"
},
"extract_usage_history_for_interval": {
"default": "30 days",
"description": "Used only if extract_usage_history is set to True. Interval to extract looker dashboard usage history for. See https://docs.looker.com/reference/filter-expressions#date_and_time.",
"title": "Extract Usage History For Interval",
"type": "string"
},
"extract_embed_urls": {
"default": true,
"description": "Produce URLs used to render Looker Explores as Previews inside of DataHub UI. Embeds must be enabled inside of Looker to use this feature.",
"title": "Extract Embed Urls",
"type": "boolean"
},
"extract_independent_looks": {
"default": false,
"description": "Extract looks which are not part of any Dashboard. To enable this flag the stateful_ingestion should also be enabled.",
"title": "Extract Independent Looks",
"type": "boolean"
},
"emit_used_explores_only": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, only explores that are used by a Dashboard/Look will be ingested.",
"title": "Emit Used Explores Only",
"type": "boolean"
},
"include_platform_instance_in_urns": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, platform instance will be added in dashboard and chart urn.",
"title": "Include Platform Instance In Urns",
"type": "boolean"
},
"folder_path_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/AllowDenyPattern",
"default": {
"allow": [
".*"
],
"deny": [],
"ignoreCase": true
},
"description": "Allow or deny dashboards from specific folders using their fully qualified paths. For example: \ndeny: \n - Shared/deprecated \nThis pattern will deny the ingestion of all dashboards and looks within the Shared/deprecated folder. \nallow: \n - Shared/sales \nThis pattern will allow only the ingestion of dashboards within the Shared/sales folder. \nTo get the correct path from Looker, take the folder hierarchy shown in the UI and join it with slashes. For example, Shared -> Customer Reports -> Sales becomes Shared/Customer Reports/Sales. Dashboards will only be ingested if they're allowed by both this config and dashboard_pattern."
}
},
"required": [
"client_id",
"client_secret",
"base_url"
],
"title": "LookerDashboardSourceConfig",
"type": "object"
}
Code Coordinates
- Class Name:
datahub.ingestion.source.looker.looker_source.LookerDashboardSource - Browse on GitHub
Module lookml
Important Capabilities
| Capability | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Containers | ✅ | Enabled by default. Supported for types - LookML Project. |
| Column-level Lineage | ✅ | Enabled by default, configured using extract_column_level_lineage. |
| Detect Deleted Entities | ✅ | Enabled by default via stateful ingestion. |
| Platform Instance | ✅ | Use the platform_instance and connection_to_platform_map fields. |
| Table-Level Lineage | ✅ | Supported by default. |
This plugin extracts the following:
- LookML views from model files in a project
- Name, upstream table names, metadata for dimensions, measures, and dimension groups attached as tags
- If API integration is enabled (recommended), resolves table and view names by calling the Looker API, otherwise supports offline resolution of these names.
To get complete Looker metadata integration (including Looker dashboards and charts and lineage to the underlying Looker views, you must ALSO use the looker source module.
Prerequisites
[Recommended] Create a GitHub Deploy Key
To use LookML ingestion through the UI, or automate github checkout through the cli, you must set up a GitHub deploy key for your Looker GitHub repository. Read this document for how to set up deploy keys for your Looker git repo.
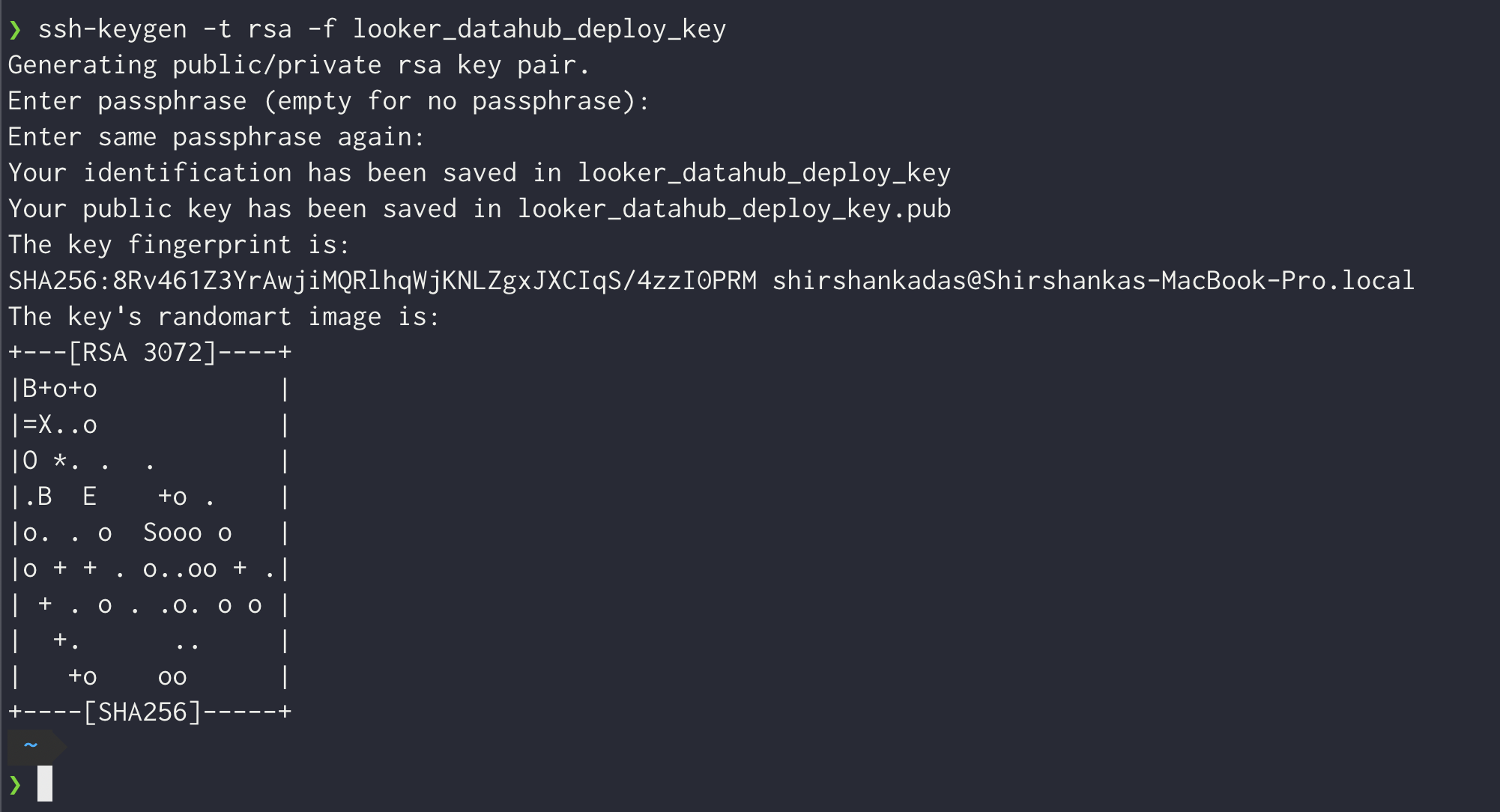
In a nutshell, there are three steps:
Generate a private-public ssh key pair. This will typically generate two files, e.g. looker_datahub_deploy_key (this is the private key) and looker_datahub_deploy_key.pub (this is the public key). Do not add a passphrase.
Add the public key to your Looker git repo as a deploy key with read access (no need to provision write access). Follow the guide here for that.
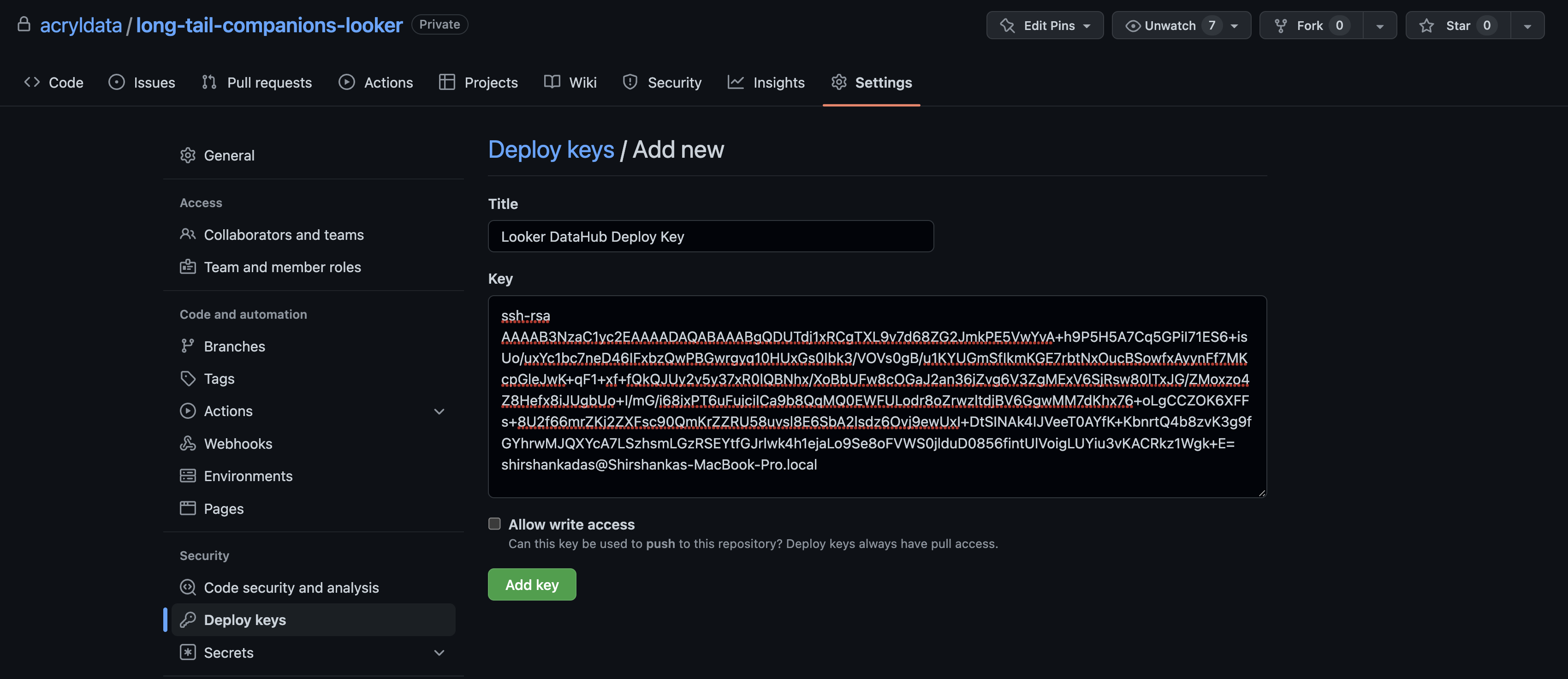
Make note of the private key file, you will need to paste the contents of the file into the GitHub Deploy Key field later while setting up ingestion using the UI.
Setup your connection mapping
The connection mapping enables DataHub to accurately generate lineage to your upstream warehouse. It maps Looker connection names to the platform and database that they're pointing to.
There's two ways to configure this:
- Provide Looker admin API credentials, and we'll automatically map lineage correctly. Details on how to do this are below.
- Manually populate the
connection_to_platform_mapandproject_nameconfiguration fields. See the starter recipe for an example of what this should look like.
[Optional] Create an API key with admin privileges
See the Looker authentication docs for the steps to create a client ID and secret. You need to ensure that the API key is attached to a user that has Admin privileges.
If you don't want to provide admin API credentials, you can manually populate the connection_to_platform_map and project_name in the ingestion configuration.
Ingestion Options
You have 3 options for controlling where your ingestion of LookML is run.
- The DataHub UI (recommended for the easiest out-of-the-box experience)
- As a GitHub Action (recommended to ensure that you have the freshest metadata pushed on change)
- Using the CLI (scheduled via an orchestrator like Airflow)
Read on to learn more about these options.
UI-based Ingestion [Recommended for ease of use]
To ingest LookML metadata through the UI, you must set up a GitHub deploy key using the instructions in the section above. Once that is complete, you can follow the on-screen instructions to set up a LookML source using the Ingestion page. The following video shows you how to ingest LookML metadata through the UI and find the relevant information from your Looker account.
GitHub Action based Ingestion [Recommended for push-based integration]
You can set up ingestion using a GitHub Action to push metadata whenever your main Looker GitHub repo changes. The following sample GitHub action file can be modified to emit LookML metadata whenever there is a change to your repository. This ensures that metadata is already fresh and up to date.
Sample GitHub Action
Drop this file into your .github/workflows directory inside your Looker GitHub repo.
You need to set up the following secrets in your GitHub repository to get this workflow to work:
- DATAHUB_GMS_HOST: The endpoint where your DataHub host is running
- DATAHUB_TOKEN: An authentication token provisioned for DataHub ingestion
- LOOKER_BASE_URL: The base url where your Looker assets are hosted (e.g. https://acryl.cloud.looker.com)
- LOOKER_CLIENT_ID: A provisioned Looker Client ID
- LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET: A provisioned Looker Client Secret
name: lookml metadata upload
on:
# Note that this action only runs on pushes to your main branch. If you want to also
# run on pull requests, we'd recommend running datahub ingest with the `--dry-run` flag.
push:
branches:
- main
release:
types: [published, edited]
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
lookml-metadata-upload:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.10"
- name: Run LookML ingestion
run: |
pip install 'acryl-datahub[lookml,datahub-rest]'
cat << EOF > lookml_ingestion.yml
# LookML ingestion configuration.
# This is a full ingestion recipe, and supports all config options that the LookML source supports.
source:
type: "lookml"
config:
base_folder: ${{ github.workspace }}
parse_table_names_from_sql: true
git_info:
repo: ${{ github.repository }}
branch: ${{ github.ref }}
# Options
#connection_to_platform_map:
# connection-name:
# platform: platform-name (e.g. snowflake)
# default_db: default-db-name (e.g. DEMO_PIPELINE)
api:
client_id: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET}
base_url: ${LOOKER_BASE_URL}
# Enable API-based lineage extraction (required for field splitting features)
use_api_for_view_lineage: true
# Optional: Large view handling configuration
# field_threshold_for_splitting: 100
# allow_partial_lineage_results: true
# enable_individual_field_fallback: true
# max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 10
sink:
type: datahub-rest
config:
server: ${DATAHUB_GMS_URL}
token: ${DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN}
EOF
datahub ingest -c lookml_ingestion.yml
env:
DATAHUB_GMS_URL: ${{ secrets.DATAHUB_GMS_URL }}
DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN }}
LOOKER_BASE_URL: ${{ secrets.LOOKER_BASE_URL }}
LOOKER_CLIENT_ID: ${{ secrets.LOOKER_CLIENT_ID }}
LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET: ${{ secrets.LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET }}
If you want to ingest lookml using the datahub cli directly, read on for instructions and configuration details.
CLI based Ingestion
Starter Recipe
Check out the following recipe to get started with ingestion! See below for full configuration options.
For general pointers on writing and running a recipe, see our main recipe guide.
source:
type: "lookml"
config:
# GitHub Coordinates: Used to check out the repo locally and add github links on the dataset's entity page.
git_info:
repo: org/repo-name
deploy_key_file: ${LOOKER_DEPLOY_KEY_FILE} # file containing the private ssh key for a deploy key for the looker git repo
# Coordinates
# base_folder: /path/to/model/files ## Optional if you are not able to provide a GitHub deploy key
# Options
api:
# Coordinates for your looker instance
base_url: "https://YOUR_INSTANCE.cloud.looker.com"
# Credentials for your Looker connection (https://docs.looker.com/reference/api-and-integration/api-auth)
client_id: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET}
# Enable API-based lineage extraction (REQUIRED for field splitting features)
# When enabled, uses Looker API to get SQL representation of views for lineage parsing
# This enables field splitting, parallel processing, and individual field fallback for large views
# NOTE: Only works for "reachable views" - views that are referenced by explores in model files
# Unreachable views will fall back to regex-based parsing
use_api_for_view_lineage: true
# Control whether unreachable views are processed
# If true (default), only views referenced by explores are processed
# If false, all views are processed, but unreachable ones use regex parsing instead of API
# emit_reachable_views_only: true
# Optional: Enable API caching for better performance
# use_api_cache_for_view_lineage: true
# Large View Handling (for views with 100+ fields)
# These options help handle large views with many fields by splitting them into chunks
# and processing in parallel for better performance and reliability
# NOTE: Requires 'api' configuration and 'use_api_for_view_lineage: true' to work
# field_threshold_for_splitting: 100 # Split views with more than this many fields (default: 100)
# allow_partial_lineage_results: true # Return partial lineage if some chunks fail (default: true)
# enable_individual_field_fallback: true # Process fields individually if chunk fails (default: true)
# max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 10 # Parallel workers for processing (default: 10, max: 100)
# Alternative to API section above if you want a purely file-based ingestion with no api calls to Looker or if you want to provide platform_instance ids for your connections
# project_name: PROJECT_NAME # See (https://docs.looker.com/data-modeling/getting-started/how-project-works) to understand what is your project name
# connection_to_platform_map:
# connection_name_1:
# platform: snowflake # bigquery, hive, etc
# default_db: DEFAULT_DATABASE. # the default database configured for this connection
# default_schema: DEFAULT_SCHEMA # the default schema configured for this connection
# platform_instance: snow_warehouse # optional
# platform_env: PROD # optional
# connection_name_2:
# platform: bigquery # snowflake, hive, etc
# default_db: DEFAULT_DATABASE. # the default database configured for this connection
# default_schema: DEFAULT_SCHEMA # the default schema configured for this connection
# platform_instance: bq_warehouse # optional
# platform_env: DEV # optional
# Default sink is datahub-rest and doesn't need to be configured
# See https://docs.datahub.com/docs/metadata-ingestion/sink_docs/datahub for customization options
Config Details
- Options
- Schema
Note that a . is used to denote nested fields in the YAML recipe.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
allow_partial_lineage_results boolean | When enabled, allows partial lineage results to be returned even when some field chunks fail or when there are SQL parsing errors. This provides better resilience for large field sets and ensures some lineage information is available rather than complete failure. Default: True |
base_folder One of string(directory-path), null | Required if not providing github configuration and deploy keys. A pointer to a local directory (accessible to the ingestion system) where the root of the LookML repo has been checked out (typically via a git clone). This is typically the root folder where the *.model.lkml and *.view.lkml files are stored. e.g. If you have checked out your LookML repo under /Users/jdoe/workspace/my-lookml-repo, then set base_folder to /Users/jdoe/workspace/my-lookml-repo. Default: None |
emit_reachable_views_only boolean | When enabled, only views that are reachable from explores defined in the model files are emitted. If set to False, all views imported in model files are emitted. Views that are unreachable i.e. not explicitly defined in the model files are currently not emitted however reported as warning for debugging purposes. Default: True |
enable_individual_field_fallback boolean | When enabled, if a field chunk fails, the system will attempt to process each field individually to maximize information and isolate problematic fields. This helps identify which specific fields are causing issues while still getting lineage for working fields. Default: True |
extract_column_level_lineage boolean | When enabled, extracts column-level lineage from Views and Explores Default: True |
field_threshold_for_splitting integer | When the total number of fields returned by Looker API exceeds this threshold, the fields will be split into multiple API calls to avoid SQL parsing failures. This helps provide partial column and table lineage when dealing with large field sets. Default: 100 |
liquid_variables object | A dictionary containing Liquid variables with their corresponding values, utilized in SQL-defined derived views. The Liquid template will be resolved in view.derived_table.sql and view.sql_table_name. Defaults to an empty dictionary. Default: {} |
looker_environment Enum | One of: "prod", "dev" Default: prod |
lookml_constants map(str,string) | |
max_file_snippet_length integer | When extracting the view definition from a lookml file, the maximum number of characters to extract. Default: 512000 |
max_workers_for_parallel_processing integer | Maximum number of worker threads to use for parallel processing of field chunks and individual fields. Set to 1 to process everything sequentially. Higher values can improve performance but may increase memory usage. Maximum allowed value is 100 to prevent resource exhaustion. Default: 10 |
parse_table_names_from_sql boolean | See note below. Default: True |
platform_instance One of string, null | The instance of the platform that all assets produced by this recipe belong to. This should be unique within the platform. See https://docs.datahub.com/docs/platform-instances/ for more details. Default: None |
populate_sql_logic_for_missing_descriptions boolean | When enabled, field descriptions will include the sql logic for computed fields if descriptions are missing Default: False |
process_isolation_for_sql_parsing boolean | When enabled, sql parsing will be executed in a separate process to prevent memory leaks. Default: False |
process_refinements boolean | When enabled, looker refinement will be processed to adapt an existing view. Default: False |
project_name One of string, null | Required if you don't specify the api section. The project name within which all the model files live. See (https://docs.looker.com/data-modeling/getting-started/how-project-works) to understand what the Looker project name should be. The simplest way to see your projects is to click on Develop followed by Manage LookML Projects in the Looker application. Default: None |
tag_measures_and_dimensions boolean | When enabled, attaches tags to measures, dimensions and dimension groups to make them more discoverable. When disabled, adds this information to the description of the column. Default: True |
use_api_cache_for_view_lineage boolean | When enabled, uses Looker API server-side caching for query execution. Requires 'api' configuration to be provided. Default: False |
use_api_for_view_lineage boolean | When enabled, uses Looker API to get SQL representation of views for lineage parsing instead of parsing LookML files directly. Requires 'api' configuration to be provided.Coverage of regex based lineage extraction has limitations, it only supportes ${TABLE}.column_name syntax, See (https://cloud.google.com/looker/docs/reference/param-field-sql#sql_for_dimensions) tounderstand the other substitutions and cross-references allowed in LookML. Default: False |
env string | The environment that all assets produced by this connector belong to Default: PROD |
api One of LookerAPIConfig, null | Default: None |
api.base_url ❓ string | Url to your Looker instance: https://company.looker.com:19999 or https://looker.company.com, or similar. Used for making API calls to Looker and constructing clickable dashboard and chart urls. |
api.client_id ❓ string | Looker API client id. |
api.client_secret ❓ string(password) | Looker API client secret. |
api.max_retries integer | Number of retries for Looker API calls Default: 3 |
api.transport_options One of TransportOptionsConfig, null | Populates the TransportOptions struct for looker client Default: None |
api.transport_options.headers ❓ map(str,string) | |
api.transport_options.timeout ❓ integer | |
connection_to_platform_map One of LookerConnectionDefinition, null | A mapping of Looker connection names to DataHub platform, database, and schema values. Default: None |
connection_to_platform_map. key.platform ❓string | |
connection_to_platform_map. key.default_db ❓string | |
connection_to_platform_map. key.default_schemaOne of string, null | Default: None |
connection_to_platform_map. key.platform_envOne of string, null | The environment that the platform is located in. Leaving this empty will inherit defaults from the top level Looker configuration Default: None |
connection_to_platform_map. key.platform_instanceOne of string, null | Default: None |
explore_browse_pattern LookerNamingPattern | |
explore_browse_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
explore_naming_pattern LookerNamingPattern | |
explore_naming_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
git_info One of GitInfo, null | Reference to your git location. If present, supplies handy links to your lookml on the dataset entity page. Default: None |
git_info.repo ❓ string | Name of your Git repo e.g. https://github.com/datahub-project/datahub or https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab. If organization/repo is provided, we assume it is a GitHub repo. |
git_info.branch string | Branch on which your files live by default. Typically main or master. This can also be a commit hash. Default: main |
git_info.deploy_key One of string(password), null | A private key that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. See deploy_key_file if you want to use a file that contains this key. Default: None |
git_info.deploy_key_file One of string(file-path), null | A private key file that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. Use a file where possible, else see deploy_key for a config field that accepts a raw string. We expect the key not have a passphrase. Default: None |
git_info.repo_ssh_locator One of string, null | The url to call git clone on. We infer this for github and gitlab repos, but it is required for other hosts. Default: None |
git_info.url_subdir One of string, null | Prefix to prepend when generating URLs for files - useful when files are in a subdirectory. Only affects URL generation, not git operations. Default: None |
git_info.url_template One of string, null | Template for generating a URL to a file in the repo e.g. '{repo_url}/blob/{branch}/{file_path}'. We can infer this for GitHub and GitLab repos, and it is otherwise required.It supports the following variables: {repo_url}, {branch}, {file_path} Default: None |
model_pattern AllowDenyPattern | A class to store allow deny regexes |
model_pattern.ignoreCase One of boolean, null | Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching. Default: True |
project_dependencies One of map(str,union)(directory-path), map(str,union) | |
project_dependencies. key.repo ❓string | Name of your Git repo e.g. https://github.com/datahub-project/datahub or https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab. If organization/repo is provided, we assume it is a GitHub repo. |
project_dependencies. key.branchstring | Branch on which your files live by default. Typically main or master. This can also be a commit hash. Default: main |
project_dependencies. key.deploy_keyOne of string(password), null | A private key that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. See deploy_key_file if you want to use a file that contains this key. Default: None |
project_dependencies. key.deploy_key_fileOne of string(file-path), null | A private key file that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. Use a file where possible, else see deploy_key for a config field that accepts a raw string. We expect the key not have a passphrase. Default: None |
project_dependencies. key.repo_ssh_locatorOne of string, null | The url to call git clone on. We infer this for github and gitlab repos, but it is required for other hosts. Default: None |
project_dependencies. key.url_subdirOne of string, null | Prefix to prepend when generating URLs for files - useful when files are in a subdirectory. Only affects URL generation, not git operations. Default: None |
project_dependencies. key.url_templateOne of string, null | Template for generating a URL to a file in the repo e.g. '{repo_url}/blob/{branch}/{file_path}'. We can infer this for GitHub and GitLab repos, and it is otherwise required.It supports the following variables: {repo_url}, {branch}, {file_path} Default: None |
transport_options One of TransportOptionsConfig, null | Populates the TransportOptions struct for looker client Default: None |
transport_options.headers ❓ map(str,string) | |
transport_options.timeout ❓ integer | |
view_browse_pattern LookerViewNamingPattern | |
view_browse_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
view_naming_pattern LookerViewNamingPattern | |
view_naming_pattern.pattern ❓ string | |
view_pattern AllowDenyPattern | A class to store allow deny regexes |
view_pattern.ignoreCase One of boolean, null | Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching. Default: True |
stateful_ingestion One of StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig, null | Default: None |
stateful_ingestion.enabled boolean | Whether or not to enable stateful ingest. Default: True if a pipeline_name is set and either a datahub-rest sink or datahub_api is specified, otherwise False Default: False |
stateful_ingestion.fail_safe_threshold number | Prevents large amount of soft deletes & the state from committing from accidental changes to the source configuration if the relative change percent in entities compared to the previous state is above the 'fail_safe_threshold'. Default: 75.0 |
stateful_ingestion.remove_stale_metadata boolean | Soft-deletes the entities present in the last successful run but missing in the current run with stateful_ingestion enabled. Default: True |
The JSONSchema for this configuration is inlined below.
{
"$defs": {
"AllowDenyPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "A class to store allow deny regexes",
"properties": {
"allow": {
"default": [
".*"
],
"description": "List of regex patterns to include in ingestion",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Allow",
"type": "array"
},
"deny": {
"default": [],
"description": "List of regex patterns to exclude from ingestion.",
"items": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Deny",
"type": "array"
},
"ignoreCase": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "boolean"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": true,
"description": "Whether to ignore case sensitivity during pattern matching.",
"title": "Ignorecase"
}
},
"title": "AllowDenyPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"GitInfo": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "A reference to a Git repository, including a deploy key that can be used to clone it.",
"properties": {
"repo": {
"description": "Name of your Git repo e.g. https://github.com/datahub-project/datahub or https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab. If organization/repo is provided, we assume it is a GitHub repo.",
"title": "Repo",
"type": "string"
},
"branch": {
"default": "main",
"description": "Branch on which your files live by default. Typically main or master. This can also be a commit hash.",
"title": "Branch",
"type": "string"
},
"url_subdir": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Prefix to prepend when generating URLs for files - useful when files are in a subdirectory. Only affects URL generation, not git operations.",
"title": "Url Subdir"
},
"url_template": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Template for generating a URL to a file in the repo e.g. '{repo_url}/blob/{branch}/{file_path}'. We can infer this for GitHub and GitLab repos, and it is otherwise required.It supports the following variables: {repo_url}, {branch}, {file_path}",
"title": "Url Template"
},
"deploy_key_file": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "file-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "A private key file that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. Use a file where possible, else see deploy_key for a config field that accepts a raw string. We expect the key not have a passphrase.",
"title": "Deploy Key File"
},
"deploy_key": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "password",
"type": "string",
"writeOnly": true
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "A private key that contains an ssh key that has been configured as a deploy key for this repository. See deploy_key_file if you want to use a file that contains this key.",
"title": "Deploy Key"
},
"repo_ssh_locator": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "The url to call `git clone` on. We infer this for github and gitlab repos, but it is required for other hosts.",
"title": "Repo Ssh Locator"
}
},
"required": [
"repo"
],
"title": "GitInfo",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerAPIConfig": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"client_id": {
"description": "Looker API client id.",
"title": "Client Id",
"type": "string"
},
"client_secret": {
"description": "Looker API client secret.",
"format": "password",
"title": "Client Secret",
"type": "string",
"writeOnly": true
},
"base_url": {
"description": "Url to your Looker instance: `https://company.looker.com:19999` or `https://looker.company.com`, or similar. Used for making API calls to Looker and constructing clickable dashboard and chart urls.",
"title": "Base Url",
"type": "string"
},
"transport_options": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/TransportOptionsConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Populates the [TransportOptions](https://github.com/looker-open-source/sdk-codegen/blob/94d6047a0d52912ac082eb91616c1e7c379ab262/python/looker_sdk/rtl/transport.py#L70) struct for looker client"
},
"max_retries": {
"default": 3,
"description": "Number of retries for Looker API calls",
"title": "Max Retries",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"required": [
"client_id",
"client_secret",
"base_url"
],
"title": "LookerAPIConfig",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerConnectionDefinition": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"platform": {
"title": "Platform",
"type": "string"
},
"default_db": {
"title": "Default Db",
"type": "string"
},
"default_schema": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"title": "Default Schema"
},
"platform_instance": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"title": "Platform Instance"
},
"platform_env": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "The environment that the platform is located in. Leaving this empty will inherit defaults from the top level Looker configuration",
"title": "Platform Env"
}
},
"required": [
"platform",
"default_db"
],
"title": "LookerConnectionDefinition",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerNamingPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"pattern": {
"title": "Pattern",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"pattern"
],
"title": "LookerNamingPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"LookerViewNamingPattern": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"pattern": {
"title": "Pattern",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"pattern"
],
"title": "LookerViewNamingPattern",
"type": "object"
},
"StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Base specialized config for Stateful Ingestion with stale metadata removal capability.",
"properties": {
"enabled": {
"default": false,
"description": "Whether or not to enable stateful ingest. Default: True if a pipeline_name is set and either a datahub-rest sink or `datahub_api` is specified, otherwise False",
"title": "Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"remove_stale_metadata": {
"default": true,
"description": "Soft-deletes the entities present in the last successful run but missing in the current run with stateful_ingestion enabled.",
"title": "Remove Stale Metadata",
"type": "boolean"
},
"fail_safe_threshold": {
"default": 75.0,
"description": "Prevents large amount of soft deletes & the state from committing from accidental changes to the source configuration if the relative change percent in entities compared to the previous state is above the 'fail_safe_threshold'.",
"maximum": 100.0,
"minimum": 0.0,
"title": "Fail Safe Threshold",
"type": "number"
}
},
"title": "StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig",
"type": "object"
},
"TransportOptionsConfig": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"timeout": {
"title": "Timeout",
"type": "integer"
},
"headers": {
"additionalProperties": {
"type": "string"
},
"title": "Headers",
"type": "object"
}
},
"required": [
"timeout",
"headers"
],
"title": "TransportOptionsConfig",
"type": "object"
}
},
"additionalProperties": false,
"properties": {
"platform_instance": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "The instance of the platform that all assets produced by this recipe belong to. This should be unique within the platform. See https://docs.datahub.com/docs/platform-instances/ for more details.",
"title": "Platform Instance"
},
"env": {
"default": "PROD",
"description": "The environment that all assets produced by this connector belong to",
"title": "Env",
"type": "string"
},
"stateful_ingestion": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/StatefulStaleMetadataRemovalConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": ""
},
"explore_naming_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "{model}.explore.{name}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing dataset names to explores. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name']"
},
"explore_browse_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "/Explore/{model}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing browse paths to explores. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name']"
},
"view_naming_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerViewNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "{project}.view.{name}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing dataset names to views. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name', 'file_path', 'folder_path']"
},
"view_browse_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerViewNamingPattern",
"default": {
"pattern": "/Develop/{project}/{folder_path}"
},
"description": "Pattern for providing browse paths to views. Allowed variables are ['platform', 'env', 'project', 'model', 'name', 'file_path', 'folder_path']"
},
"tag_measures_and_dimensions": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, attaches tags to measures, dimensions and dimension groups to make them more discoverable. When disabled, adds this information to the description of the column.",
"title": "Tag Measures And Dimensions",
"type": "boolean"
},
"extract_column_level_lineage": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, extracts column-level lineage from Views and Explores",
"title": "Extract Column Level Lineage",
"type": "boolean"
},
"git_info": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/GitInfo"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Reference to your git location. If present, supplies handy links to your lookml on the dataset entity page."
},
"base_folder": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "directory-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Required if not providing github configuration and deploy keys. A pointer to a local directory (accessible to the ingestion system) where the root of the LookML repo has been checked out (typically via a git clone). This is typically the root folder where the `*.model.lkml` and `*.view.lkml` files are stored. e.g. If you have checked out your LookML repo under `/Users/jdoe/workspace/my-lookml-repo`, then set `base_folder` to `/Users/jdoe/workspace/my-lookml-repo`.",
"title": "Base Folder"
},
"project_dependencies": {
"additionalProperties": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "directory-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/GitInfo"
}
]
},
"default": {},
"description": "A map of project_name to local directory (accessible to the ingestion system) or Git credentials. Every local_dependencies or private remote_dependency listed in the main project's manifest.lkml file should have a corresponding entry here. If a deploy key is not provided, the ingestion system will use the same deploy key as the main project. When providing a local directory path (string), the directory must exist at config validation time.",
"title": "Project Dependencies",
"type": "object"
},
"connection_to_platform_map": {
"anyOf": [
{
"additionalProperties": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerConnectionDefinition"
},
"type": "object"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "A mapping of [Looker connection names](https://docs.looker.com/reference/model-params/connection-for-model) to DataHub platform, database, and schema values.",
"title": "Connection To Platform Map"
},
"model_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/AllowDenyPattern",
"default": {
"allow": [
".*"
],
"deny": [],
"ignoreCase": true
},
"description": "List of regex patterns for LookML models to include in the extraction."
},
"view_pattern": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/AllowDenyPattern",
"default": {
"allow": [
".*"
],
"deny": [],
"ignoreCase": true
},
"description": "List of regex patterns for LookML views to include in the extraction."
},
"parse_table_names_from_sql": {
"default": true,
"description": "See note below.",
"title": "Parse Table Names From Sql",
"type": "boolean"
},
"use_api_for_view_lineage": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, uses Looker API to get SQL representation of views for lineage parsing instead of parsing LookML files directly. Requires 'api' configuration to be provided.Coverage of regex based lineage extraction has limitations, it only supportes ${TABLE}.column_name syntax, See (https://cloud.google.com/looker/docs/reference/param-field-sql#sql_for_dimensions) tounderstand the other substitutions and cross-references allowed in LookML.",
"title": "Use Api For View Lineage",
"type": "boolean"
},
"use_api_cache_for_view_lineage": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, uses Looker API server-side caching for query execution. Requires 'api' configuration to be provided.",
"title": "Use Api Cache For View Lineage",
"type": "boolean"
},
"api": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/LookerAPIConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null
},
"project_name": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Required if you don't specify the `api` section. The project name within which all the model files live. See (https://docs.looker.com/data-modeling/getting-started/how-project-works) to understand what the Looker project name should be. The simplest way to see your projects is to click on `Develop` followed by `Manage LookML Projects` in the Looker application.",
"title": "Project Name"
},
"transport_options": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$ref": "#/$defs/TransportOptionsConfig"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"description": "Populates the [TransportOptions](https://github.com/looker-open-source/sdk-codegen/blob/94d6047a0d52912ac082eb91616c1e7c379ab262/python/looker_sdk/rtl/transport.py#L70) struct for looker client"
},
"max_file_snippet_length": {
"default": 512000,
"description": "When extracting the view definition from a lookml file, the maximum number of characters to extract.",
"title": "Max File Snippet Length",
"type": "integer"
},
"emit_reachable_views_only": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, only views that are reachable from explores defined in the model files are emitted. If set to False, all views imported in model files are emitted. Views that are unreachable i.e. not explicitly defined in the model files are currently not emitted however reported as warning for debugging purposes.",
"title": "Emit Reachable Views Only",
"type": "boolean"
},
"populate_sql_logic_for_missing_descriptions": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, field descriptions will include the sql logic for computed fields if descriptions are missing",
"title": "Populate Sql Logic For Missing Descriptions",
"type": "boolean"
},
"process_isolation_for_sql_parsing": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, sql parsing will be executed in a separate process to prevent memory leaks.",
"title": "Process Isolation For Sql Parsing",
"type": "boolean"
},
"process_refinements": {
"default": false,
"description": "When enabled, looker refinement will be processed to adapt an existing view.",
"title": "Process Refinements",
"type": "boolean"
},
"liquid_variables": {
"additionalProperties": true,
"default": {},
"description": "A dictionary containing Liquid variables with their corresponding values, utilized in SQL-defined derived views. The Liquid template will be resolved in view.derived_table.sql and view.sql_table_name. Defaults to an empty dictionary.",
"title": "Liquid Variables",
"type": "object"
},
"lookml_constants": {
"additionalProperties": {
"type": "string"
},
"default": {},
"description": "A dictionary containing LookML constants (`@{constant_name}`) and their values. If a constant is defined in the `manifest.lkml` file, its value will be used. If not found in the manifest, the value from this config will be used instead. Defaults to an empty dictionary.",
"title": "Lookml Constants",
"type": "object"
},
"looker_environment": {
"default": "prod",
"description": "A looker prod or dev environment. It helps to evaluate looker if comments i.e. -- if prod --. All if comments are evaluated to true for configured looker_environment value",
"enum": [
"prod",
"dev"
],
"title": "Looker Environment",
"type": "string"
},
"field_threshold_for_splitting": {
"default": 100,
"description": "When the total number of fields returned by Looker API exceeds this threshold, the fields will be split into multiple API calls to avoid SQL parsing failures. This helps provide partial column and table lineage when dealing with large field sets.",
"title": "Field Threshold For Splitting",
"type": "integer"
},
"allow_partial_lineage_results": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, allows partial lineage results to be returned even when some field chunks fail or when there are SQL parsing errors. This provides better resilience for large field sets and ensures some lineage information is available rather than complete failure.",
"title": "Allow Partial Lineage Results",
"type": "boolean"
},
"enable_individual_field_fallback": {
"default": true,
"description": "When enabled, if a field chunk fails, the system will attempt to process each field individually to maximize information and isolate problematic fields. This helps identify which specific fields are causing issues while still getting lineage for working fields.",
"title": "Enable Individual Field Fallback",
"type": "boolean"
},
"max_workers_for_parallel_processing": {
"default": 10,
"description": "Maximum number of worker threads to use for parallel processing of field chunks and individual fields. Set to 1 to process everything sequentially. Higher values can improve performance but may increase memory usage. Maximum allowed value is 100 to prevent resource exhaustion.",
"title": "Max Workers For Parallel Processing",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"title": "LookMLSourceConfig",
"type": "object"
}
Configuration Notes
API-Based Lineage Extraction and Reachable Views
When use_api_for_view_lineage: true is enabled, DataHub uses the LookerQueryAPIBasedViewUpstream implementation to extract lineage. This approach:
Uses SQL from Looker API: The system queries the Looker API to generate fully resolved SQL statements for views, which are then parsed to extract column-level and table-level lineage. This provides more accurate lineage than regex-based parsing.
Works Only for Reachable Views: The Looker Query API requires an explore name to generate SQL queries. Therefore, this method only works for views that are reachable from explores defined in your LookML model files. A view is considered "reachable" if it is referenced by at least one explore (either directly or through joins).
Fallback Behavior: Views that are not reachable from any explore cannot use the API-based approach and will automatically fall back to regex-based parsing. If
emit_reachable_views_only: true(default), unreachable views are skipped entirely.
Example:
source:
type: lookml
config:
# Enable API-based lineage (requires reachable views)
use_api_for_view_lineage: true
# Control whether unreachable views are processed
# If true (default), only views referenced by explores are processed
# If false, all views are processed, but unreachable ones use regex parsing
emit_reachable_views_only: true
When a view is not reachable:
- If
emit_reachable_views_only: true: The view is skipped and a warning is logged - If
emit_reachable_views_only: false: The view is processed using regex-based parsing (may have limited lineage accuracy)
Liquid Template Support and Limitations
Handling Liquid Templates
If a view contains a liquid template, for example:
sql_table_name: {{ user_attributes['db'] }}.kafka_streaming.eventswhere
db=ANALYTICS_PROD, you need to specify the values of those variables in the liquid_variables configuration as shown below:liquid_variables:
user_attributes:
db: ANALYTICS_PRODResolving LookML Constants
If a view contains a LookML constant, for example:
sql_table_name: @{db}.kafka_streaming.events;Ingestion attempts to resolve it's value by looking at project manifest files
manifest.lkml
constant: db {
value: "ANALYTICS_PROD"
}If the constant's value is not resolved or incorrectly resolved, you can specify
lookml_constantsconfiguration in ingestion recipe as shown below. The constant value in recipe takes precedence over constant values resolved from manifest.```yml
lookml_constants:
db: ANALYTICS_PROD
```
Limitations:
- Supported: Simple variable interpolation (
{{ var }}) and condition directives ({% condition filter_name %} field {% endcondition %}) - Unsupported: Conditional logic with
if/else/endifand custom Looker tags likedate_start,date_end, andparameter
Additional Notes
Important: Unsupported templates may cause lineage extraction to fail for some assets.
Although liquid variables and LookML constants can be used anywhere in LookML code, their values are currently resolved only for LookML views by DataHub LookML ingestion. This behavior is sufficient since LookML ingestion processes only views and their upstream dependencies.
Multi-Project LookML (Advanced)
Looker projects support organization as multiple git repos, with remote includes that can refer to projects that are stored in a different repo. If your Looker implementation uses multi-project setup, you can configure the LookML source to pull in metadata from your remote projects as well.
If you are using local or remote dependencies, you will see include directives in your lookml files that look like this:
include: "//e_flights/views/users.view.lkml"
include: "//e_commerce/public/orders.view.lkml"
Also, you will see projects that are being referred to listed in your manifest.lkml file. Something like this:
project_name: this_project
local_dependency: {
project: "my-remote-project"
}
remote_dependency: ga_360_block {
url: "https://github.com/llooker/google_ga360"
ref: "0bbbef5d8080e88ade2747230b7ed62418437c21"
}
To ingest Looker repositories that are including files defined in other projects, you will need to use the project_dependencies directive within the configuration section.
Consider the following scenario:
- Your primary project refers to a remote project called
my_remote_project - The remote project is homed in the GitHub repo
my_org/my_remote_project - You have provisioned a GitHub deploy key and stored the credential in the environment variable (or UI secret),
${MY_REMOTE_PROJECT_DEPLOY_KEY}
In this case, you can add this section to your recipe to activate multi-project LookML ingestion.
source:
type: lookml
config:
... other config variables
project_dependencies:
my_remote_project:
repo: my_org/my_remote_project
deploy_key: ${MY_REMOTE_PROJECT_DEPLOY_KEY}
Under the hood, DataHub will check out your remote repository using the provisioned deploy key, and use it to navigate includes that you have in the model files from your primary project.
If you have the remote project checked out locally, and do not need DataHub to clone the project for you, you can provide DataHub directly with the path to the project like the config snippet below:
source:
type: lookml
config:
... other config variables
project_dependencies:
my_remote_project: /path/to/local_git_clone_of_remote_project
This is not the same as ingesting the remote project as a primary Looker project because DataHub will not be processing the model files that might live in the remote project. If you want to additionally include the views accessible via the models in the remote project, create a second recipe where your remote project is the primary project.
Handling Large Views with Many Fields
For Looker views with a large number of fields (100+), DataHub automatically uses field splitting to ensure reliable lineage extraction. This feature splits large field sets into manageable chunks, processes them in parallel, and combines the results.
API Configuration Required: Field splitting requires Looker API credentials to be configured. You must:
- Provide the
apiconfiguration section with your Looker credentials - Set
use_api_for_view_lineage: trueto enable API-based lineage extraction
Without API configuration, field splitting will not be available and the system will fall back to regex-based parsing, which may fail for large views.
Reachable Views Only: The LookerQueryAPIBasedViewUpstream implementation (used for field splitting) works by querying the Looker API to generate SQL statements for views. This approach only works for reachable views - views that are referenced by explores defined in your LookML model files. Views that are not reachable from any explore cannot be queried via the Looker API and will fall back to regex-based parsing. The emit_reachable_views_only configuration option controls whether only reachable views are processed.
When Field Splitting is Used
Field splitting is automatically triggered when:
use_api_for_view_lineage: trueis set- Looker API credentials are provided
- A view has more fields than the configured threshold (default: 100 fields)
You can adjust this threshold based on your needs:
source:
type: lookml
config:
# Adjust the threshold for field splitting (default: 100)
field_threshold_for_splitting: 100
When to adjust the threshold:
- Lower the threshold (e.g., 50) if you experience SQL parsing failures with views that have 50-100 fields
- Raise the threshold (e.g., 150) if your views consistently have 100+ fields and you want to minimize API calls
Partial Lineage Results
By default, DataHub will return partial lineage results even if some field chunks fail to parse. This ensures you get lineage information for working fields rather than complete failure.
source:
type: lookml
config:
# Allow partial lineage when some chunks fail (default: true)
allow_partial_lineage_results: true
When to disable:
- Set to
falseif you want strict validation and prefer complete failure over partial results - Useful for debugging to identify problematic views that need attention
Individual Field Fallback
When a chunk of fields fails, DataHub can automatically attempt to process each field individually. This helps:
- Maximize lineage extraction by processing working fields
- Identify specific problematic fields that cause issues
- Provide detailed reporting on which fields fail
source:
type: lookml
config:
# Enable individual field processing when chunks fail (default: true)
enable_individual_field_fallback: true
When to disable:
- Set to
falseif you want faster processing and don't need to identify problematic fields - Useful if you know all fields in a view are valid and want to skip the fallback overhead
Parallel Processing Performance
Field chunks are processed in parallel to improve performance. You can control the number of worker threads:
source:
type: lookml
config:
# Number of parallel workers (default: 10, max: 100)
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 10
Performance tuning:
- Increase workers (e.g., 20-30) for faster processing if you have many large views and sufficient system resources
- Decrease workers (e.g., 5) if you're hitting API rate limits or have limited system resources
- Set to 1 to process sequentially (useful for debugging)
Important: The maximum allowed value is 100 to prevent resource exhaustion. Values above 100 will be automatically capped with a warning.
Complete Configuration Example
Here's a complete example configuration for handling large views:
source:
type: lookml
config:
base_folder: /path/to/lookml
# API configuration (REQUIRED for field splitting)
api:
base_url: "https://your-instance.cloud.looker.com"
client_id: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET}
# Enable API-based lineage extraction (REQUIRED for field splitting)
use_api_for_view_lineage: true
# Optional: Enable API caching for better performance
use_api_cache_for_view_lineage: true
# Large view handling configuration
field_threshold_for_splitting: 100 # Split views with >100 fields
allow_partial_lineage_results: true # Return partial results on errors
enable_individual_field_fallback: true # Process fields individually on chunk failure
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 10 # Parallel processing workers
Important Notes:
- The
apisection with credentials is required for field splitting to work use_api_for_view_lineage: truemust be set to enable API-based lineage extraction- Without API configuration, field splitting features are not available
- Reachable Views Only: Field splitting via
LookerQueryAPIBasedViewUpstreamonly works for views that are reachable from explores. The Looker Query API requires an explore name to generate SQL, so views not referenced by any explore will use regex-based parsing instead - The
emit_reachable_views_onlyconfiguration (default:true) controls whether unreachable views are processed at all
Check ingestion logs for:
- Field splitting statistics:
View 'view_name' has X fields, exceeding threshold of Y. Splitting into multiple queries - Success rates:
Combined results for view 'view_name': X tables, Y column lineages, success rate: Z% - Problematic fields: Warnings about specific fields that fail processing
Common issues:
- Field splitting not working: Verify
use_api_for_view_lineage: trueand API credentials are configured - Low success rate (<50%): Consider lowering
field_threshold_for_splittingor investigating problematic fields - API rate limiting: Reduce
max_workers_for_parallel_processingto decrease concurrent requests - Memory issues: Reduce
max_workers_for_parallel_processingif you experience memory pressure
Troubleshooting Large View Lineage Extraction
If you have Looker views with many fields (100+) and are experiencing lineage extraction issues, the following troubleshooting steps can help:
Prerequisites: Field splitting requires Looker API configuration. Ensure you have:
apisection with valid credentials configureduse_api_for_view_lineage: trueenabled
Issue: Field splitting not working
Symptoms:
- Large views still fail even with field splitting configuration
- No field splitting messages in logs
- Views fall back to regex-based parsing
Solutions:
Verify API configuration:
source:
type: lookml
config:
api:
base_url: "https://your-instance.cloud.looker.com"
client_id: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_ID}
client_secret: ${LOOKER_CLIENT_SECRET}
use_api_for_view_lineage: true # Must be enabledCheck API credentials:
- Verify credentials have admin privileges (required for API access)
- Test API connection separately if needed
- Check logs for authentication errors
Verify view-to-explore mapping:
- Field splitting requires views to be mapped to explores (views must be reachable from explores)
- Check logs for warnings about missing explore mappings
- Ensure your views are referenced by at least one explore in your model files
- If
emit_reachable_views_only: true(default), unreachable views are skipped entirely
Issue: Lineage extraction fails for large views
Symptoms:
- Views with 100+ fields show no lineage
- Error messages about SQL parsing failures
- Incomplete lineage information
Solutions:
Verify field splitting is working: Check your ingestion logs for messages like:
View 'your_view' has 150 fields, exceeding threshold of 100. Splitting into multiple queries for partial lineage.If you don't see this message, field splitting may not be triggered. Lower the threshold:
field_threshold_for_splitting: 50 # Lower thresholdCheck success rates: Look for statistics in logs:
Combined results for view 'your_view': 5 tables, 120 column lineages, success rate: 80.0%- High success rate (>80%): System is working well
- Medium success rate (50-80%): Some fields may be problematic, but partial lineage is available
- Low success rate (<50%): Consider investigating specific fields or lowering threshold
Enable individual field fallback: If chunks are failing, enable individual field processing to identify problematic fields:
enable_individual_field_fallback: trueCheck logs for warnings about specific fields that fail.
Adjust parallel processing: If you're hitting API rate limits, reduce workers:
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 5 # Reduce from default 10
Issue: Slow processing for large views
Symptoms:
- Ingestion takes a long time for views with many fields
- Processing appears sequential
Solutions:
Increase parallel workers:
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 20 # Increase from default 10Note: Monitor system resources and API rate limits
Enable API caching:
use_api_cache_for_view_lineage: true # Enable server-side cachingVerify parallel processing is active: Check logs for concurrent processing indicators. If processing appears sequential, verify
max_workers_for_parallel_processingis set correctly.
Issue: Memory or resource exhaustion
Symptoms:
- Ingestion process runs out of memory
- System becomes unresponsive during ingestion
Solutions:
Reduce parallel workers:
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 5 # Reduce concurrent processingProcess sequentially:
max_workers_for_parallel_processing: 1 # Disable parallel processingIncrease chunk size:
field_threshold_for_splitting: 150 # Larger chunks = fewer concurrent operations
Issue: Incomplete lineage for some fields
Symptoms:
- Some fields show lineage, others don't
- Partial lineage information available
Solutions:
This is expected behavior when
allow_partial_lineage_results: true(default)- Partial lineage is better than no lineage
- Check logs for specific fields that fail
To identify problematic fields:
- Enable
enable_individual_field_fallback: true(default) - Check logs for warnings about specific fields
- Review those fields in Looker to identify issues
- Enable
For strict validation:
allow_partial_lineage_results: false # Fail completely if any chunk failsNote: This may result in no lineage for large views if any chunk fails
Best Practices
- Start with defaults: The default configuration works well for most cases
- Monitor logs: Check field splitting statistics and success rates
- Tune gradually: Adjust one parameter at a time and monitor results
- Consider your environment:
- High-resource systems: Can increase
max_workers_for_parallel_processing - Rate-limited APIs: Should decrease
max_workers_for_parallel_processing - Many problematic fields: Enable
enable_individual_field_fallback - Strict validation needs: Disable
allow_partial_lineage_results
- High-resource systems: Can increase
Debugging LookML Parsing Errors
If you see messages like my_file.view.lkml': "failed to load view file: Unable to find a matching expression for '<literal>' on line 5" in the failure logs, it indicates a parsing error for the LookML file.
The first thing to check is that the Looker IDE can validate the file without issues. You can check this by clicking this "Validate LookML" button in the IDE when in development mode.
If that's not the issue, it might be because DataHub's parser, which is based on the joshtemple/lkml library, is slightly more strict than the official Looker parser. Note that there's currently only one known discrepancy between the two parsers, and it's related to using leading colons in blocks.
To check if DataHub can parse your LookML file syntax, you can use the lkml CLI tool. If this raises an exception, DataHub will fail to parse the file.
pip install lkml
lkml path/to/my_file.view.lkml
Code Coordinates
- Class Name:
datahub.ingestion.source.looker.lookml_source.LookMLSource - Browse on GitHub
Questions
If you've got any questions on configuring ingestion for Looker, feel free to ping us on our Slack.
