Feature Store Integration With DataHub
Why Would You Integrate Feature Store with DataHub?
Feature Store is a data management layer that stores, organizes, and manages features for machine learning models. It is a centralized repository for features that can be used across different AI/ML models. By integrating Feature Store with DataHub, you can track the lineage of features used in AI/ML models, understand how features are generated, and how they are used to train models.
For technical details on feature store entities, please refer to the following docs:
Goal Of This Guide
This guide will show you how to
- Create feature store entities: MlFeature, MlFeatureTable, MlPrimaryKey
- Read feature store entities: MlFeature, MlFeatureTable, MlPrimaryKey
- Attach MlModel to MlFeature
- Attach MlFeatures to MlFeatureTable
- Attached MlFeatures to upstream Datasets that power them
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need to deploy DataHub Quickstart and ingest sample data. For detailed steps, please refer to Datahub Quickstart Guide.
Create ML Entities
For creating MLModels and MLGroups, please refer to AI/ML Integration Guide.
Create MlFeature
An ML Feature represents an instance of a feature that can be used across different machine learning models. Features are organized into Feature Tables to be consumed by machine learning models. For example, if we were modeling features for a Users Feature Table, the Features would be age, sign_up_date, active_in_past_30_days and so forth.Using Features in DataHub allows users to see the sources a feature was generated from and how a feature is used to train models.
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_create.py
import os
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
import datahub.metadata.schema_classes as models
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Create an emitter to DataHub over REST
gms_server = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_URL", "http://localhost:8080")
token = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN")
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_server, token=token)
dataset_urn = builder.make_dataset_urn(
name="fct_users_created", platform="hive", env="PROD"
)
feature_urn = builder.make_ml_feature_urn(
feature_table_name="users_feature_table",
feature_name="user_signup_date",
)
# Create feature
metadata_change_proposal = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=feature_urn,
aspect=models.MLFeaturePropertiesClass(
description="Represents the date the user created their account",
# attaching a source to a feature creates lineage between the feature
# and the upstream dataset. This is how lineage between your data warehouse
# and machine learning ecosystem is established.
sources=[dataset_urn],
dataType="TIME",
),
)
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit_mcp(metadata_change_proposal)
print(f"Created ML feature: {feature_urn}")
Note that when creating a feature, you create upstream lineage to the data warehouse using sources.
Create MlPrimaryKey
An ML Primary Key represents a specific element of a Feature Table that indicates what group the other features belong to. For example, if a Feature Table contained features for Users, the ML Primary Key would likely be user_id or some similar unique identifier for a user. Using ML Primary Keys in DataHub allow users to indicate how ML Feature Tables are structured.
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlprimarykey_create.py
import os
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
import datahub.metadata.schema_classes as models
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Create an emitter to DataHub over REST
gms_server = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_URL", "http://localhost:8080")
token = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN")
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_server, token=token)
dataset_urn = builder.make_dataset_urn(
name="fct_users_created", platform="hive", env="PROD"
)
primary_key_urn = builder.make_ml_primary_key_urn(
feature_table_name="users_feature_table",
primary_key_name="user_id",
)
# Create feature
metadata_change_proposal = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=primary_key_urn,
aspect=models.MLPrimaryKeyPropertiesClass(
description="Represents the id of the user the other features relate to.",
# attaching a source to a ml primary key creates lineage between the feature
# and the upstream dataset. This is how lineage between your data warehouse
# and machine learning ecosystem is established.
sources=[dataset_urn],
dataType="TEXT",
),
)
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit_mcp(metadata_change_proposal)
print(f"Created ML primary key: {primary_key_urn}")
Note that when creating a primary key, you create upstream lineage to the data warehouse using sources.
Create MlFeatureTable
A feature table represents a group of similar Features that can all be used together to train a model. For example, if there was a Users Feature Table, it would contain documentation around how to use the Users collection of Features and references to each Feature and ML Primary Key contained within it.
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_table_create.py
import os
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
import datahub.metadata.schema_classes as models
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Create an emitter to DataHub over REST
gms_server = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_URL", "http://localhost:8080")
token = os.getenv("DATAHUB_GMS_TOKEN")
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_server, token=token)
feature_table_urn = builder.make_ml_feature_table_urn(
feature_table_name="users_feature_table", platform="feast"
)
feature_urns = [
builder.make_ml_feature_urn(
feature_name="user_signup_date", feature_table_name="users_feature_table"
),
builder.make_ml_feature_urn(
feature_name="user_last_active_date", feature_table_name="users_feature_table"
),
]
primary_key_urns = [
builder.make_ml_primary_key_urn(
feature_table_name="users_feature_table",
primary_key_name="user_id",
)
]
feature_table_properties = models.MLFeatureTablePropertiesClass(
description="Test description",
# link your features to a feature table
mlFeatures=feature_urns,
# link your primary keys to the feature table
mlPrimaryKeys=primary_key_urns,
)
# MCP creation
metadata_change_proposal = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=feature_table_urn,
aspect=feature_table_properties,
)
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit_mcp(metadata_change_proposal)
print(f"Created ML feature table: {feature_table_urn}")
Note that when creating a feature table, you connect the table to its features and primary key using mlFeatures and mlPrimaryKeys.
Expected Outcome of creating entities
You can search the entities in DataHub UI.
Read ML Entities
Read MLFeature
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
query {
mlFeature(urn: "urn:li:mlFeature:(test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes,test_BOOL_LIST_feature)"){
name
featureNamespace
description
properties {
description
dataType
version {
versionTag
}
}
}
}
Expected response:
{
"data": {
"mlFeature": {
"name": "test_BOOL_LIST_feature",
"featureNamespace": "test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes",
"description": null,
"properties": {
"description": null,
"dataType": "SEQUENCE",
"version": null
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query": "{ mlFeature(urn: \"urn:li:mlFeature:(test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes,test_BOOL_LIST_feature)\") { name featureNamespace description properties { description dataType version { versionTag } } } }"
}'
Expected response:
{
"data": {
"mlFeature": {
"name": "test_BOOL_LIST_feature",
"featureNamespace": "test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes",
"description": null,
"properties": {
"description": null,
"dataType": "SEQUENCE",
"version": null
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_read.py
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient, MLFeatureUrn
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
# Or get this from the UI (share -> copy urn) and use MLFeatureUrn.from_string(...)
mlfeature_urn = MLFeatureUrn(
"test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes", "test_BOOL_feature"
)
mlfeature_entity = client.entities.get(mlfeature_urn)
print("MLFeature name:", mlfeature_entity.name)
print("MLFeature table:", mlfeature_entity.feature_table_urn)
print("MLFeature description:", mlfeature_entity.description)
Read MlPrimaryKey
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
query {
mlPrimaryKey(urn: "urn:li:mlPrimaryKey:(user_features,user_id)"){
name
featureNamespace
description
dataType
properties {
description
dataType
version {
versionTag
}
}
}
}
Expected response:
{
"data": {
"mlPrimaryKey": {
"name": "user_id",
"featureNamespace": "user_features",
"description": "User's internal ID",
"dataType": "ORDINAL",
"properties": {
"description": "User's internal ID",
"dataType": "ORDINAL",
"version": null
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query": "query { mlPrimaryKey(urn: \"urn:li:mlPrimaryKey:(user_features,user_id)\"){ name featureNamespace description dataType properties { description dataType version { versionTag } } }}"
}'
Expected response:
{
"data": {
"mlPrimaryKey": {
"name": "user_id",
"featureNamespace": "user_features",
"description": "User's internal ID",
"dataType": "ORDINAL",
"properties": {
"description": "User's internal ID",
"dataType": "ORDINAL",
"version": null
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlprimarykey_read.py
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient, MLPrimaryKeyUrn
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
# Or get this from the UI (share -> copy urn) and use MLPrimaryKeyUrn.from_string(...)
mlprimarykey_urn = MLPrimaryKeyUrn("user_features", "user_id")
mlprimarykey_entity = client.entities.get(mlprimarykey_urn)
print("MLPrimaryKey name:", mlprimarykey_entity.name)
print("MLPrimaryKey feature table:", mlprimarykey_entity.feature_table_urn)
print("MLPrimaryKey description:", mlprimarykey_entity.description)
Read MLFeatureTable
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
query {
mlFeatureTable(urn: "urn:li:mlFeatureTable:(urn:li:dataPlatform:feast,test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes)"){
name
description
platform {
name
}
properties {
description
mlFeatures {
name
}
}
}
}
Expected Response:
{
"data": {
"mlFeatureTable": {
"name": "test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes",
"description": null,
"platform": {
"name": "feast"
},
"properties": {
"description": null,
"mlFeatures": [
{
"name": "test_BOOL_LIST_feature"
},
...{
"name": "test_STRING_feature"
}
]
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query": "{ mlFeatureTable(urn: \"urn:li:mlFeatureTable:(urn:li:dataPlatform:feast,test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes)\") { name description platform { name } properties { description mlFeatures { name } } } }"
}'
Expected Response:
{
"data": {
"mlFeatureTable": {
"name": "test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes",
"description": null,
"platform": {
"name": "feast"
},
"properties": {
"description": null,
"mlFeatures": [
{
"name": "test_BOOL_LIST_feature"
},
...{
"name": "test_STRING_feature"
}
]
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_table_read.py
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient, MLFeatureTableUrn
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
# Or get this from the UI (share -> copy urn) and use MLFeatureTableUrn.from_string(...)
mlfeature_table_urn = MLFeatureTableUrn(
"feast", "test_feature_table_all_feature_dtypes"
)
mlfeature_table_entity = client.entities.get(mlfeature_table_urn)
print("MLFeature Table name:", mlfeature_table_entity.name)
print("MLFeature Table platform:", mlfeature_table_entity.platform)
print("MLFeature Table description:", mlfeature_table_entity.description)
Read MLModel
- GraphQL
- Curl
- Python
query {
mlModel(urn: "urn:li:mlModel:(urn:li:dataPlatform:science,scienceModel,PROD)"){
name
description
properties {
description
version
type
mlFeatures
groups {
urn
name
}
}
}
}
Expected Response:
{
"data": {
"mlModel": {
"name": "scienceModel",
"description": "A sample model for predicting some outcome.",
"properties": {
"description": "A sample model for predicting some outcome.",
"version": null,
"type": "Naive Bayes classifier",
"mlFeatures": null,
"groups": []
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"query": "{ mlModel(urn: \"urn:li:mlModel:(urn:li:dataPlatform:science,scienceModel,PROD)\") { name description properties { description version type mlFeatures groups { urn name } } } }"
}'
Expected Response:
{
"data": {
"mlModel": {
"name": "scienceModel",
"description": "A sample model for predicting some outcome.",
"properties": {
"description": "A sample model for predicting some outcome.",
"version": null,
"type": "Naive Bayes classifier",
"mlFeatures": null,
"groups": []
}
}
},
"extensions": {}
}
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlmodel_read.py
from datahub.metadata.urns import MlModelUrn
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
# Or get this from the UI (share -> copy urn) and use MlModelUrn.from_string(...)
mlmodel_urn = MlModelUrn(platform="mlflow", name="my-recommendations-model")
mlmodel_entity = client.entities.get(mlmodel_urn)
print("Model Name: ", mlmodel_entity.name)
print("Model Description: ", mlmodel_entity.description)
print("Model Group: ", mlmodel_entity.model_group)
print("Model Hyper Parameters: ", mlmodel_entity.hyper_params)
Add ML Entities
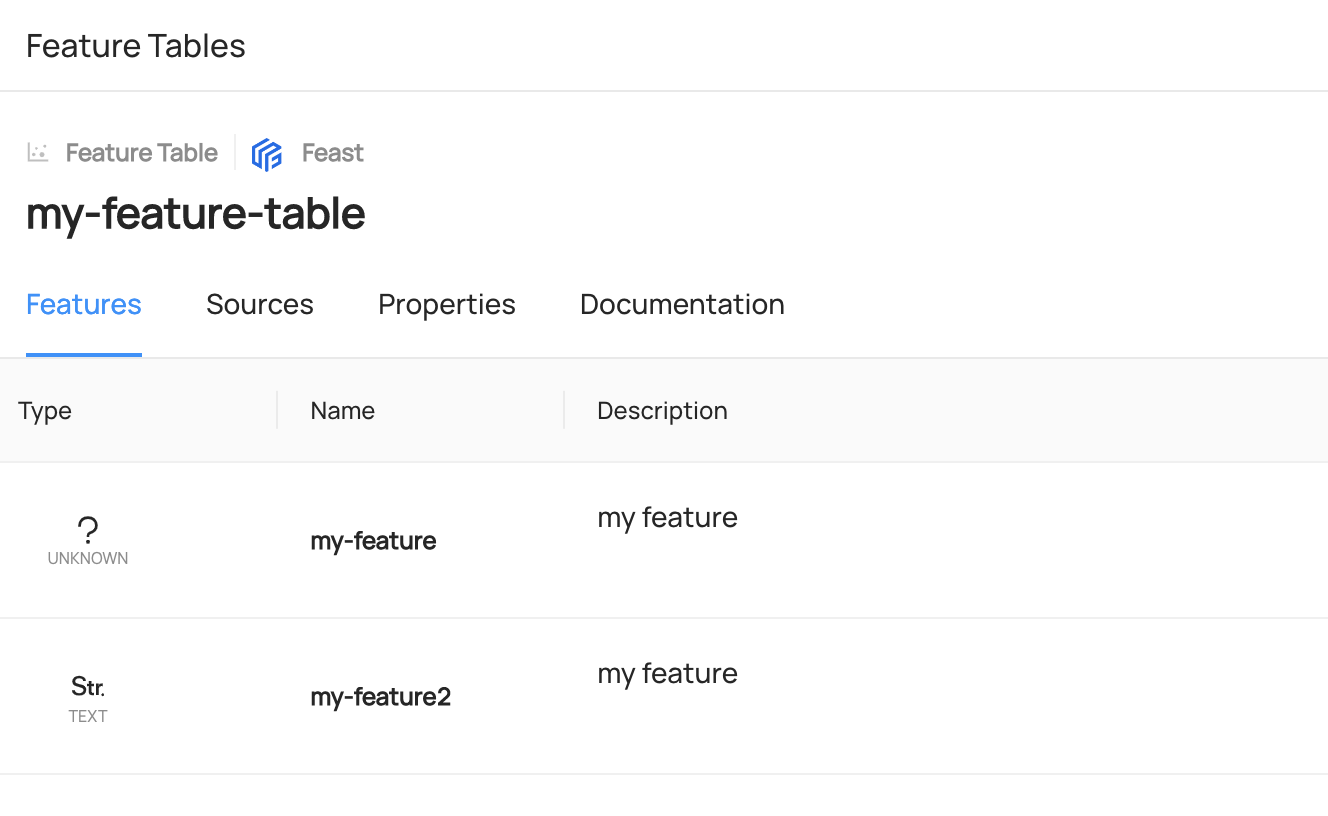
Add MlFeature to MlFeatureTable
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_add_to_mlfeature_table.py
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
import datahub.metadata.schema_classes as models
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
from datahub.ingestion.graph.client import DatahubClientConfig, DataHubGraph
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import MLFeatureTablePropertiesClass
gms_endpoint = "http://localhost:8080"
# Create an emitter to DataHub over REST
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_endpoint, extra_headers={})
feature_table_urn = builder.make_ml_feature_table_urn(
feature_table_name="my-feature-table", platform="feast"
)
feature_urns = [
builder.make_ml_feature_urn(
feature_name="my-feature2", feature_table_name="my-feature-table"
),
]
# This code concatenates the new features with the existing features in the feature table.
# If you want to replace all existing features with only the new ones, you can comment out this line.
graph = DataHubGraph(DatahubClientConfig(server=gms_endpoint))
feature_table_properties = graph.get_aspect(
entity_urn=feature_table_urn, aspect_type=MLFeatureTablePropertiesClass
)
if feature_table_properties:
current_features = feature_table_properties.mlFeatures
print("current_features:", current_features)
if current_features:
feature_urns += current_features
feature_table_properties = models.MLFeatureTablePropertiesClass(mlFeatures=feature_urns)
# MCP createion
metadata_change_proposal = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=feature_table_urn,
aspect=feature_table_properties,
)
# Emit metadata! This is a blocking call
emitter.emit(metadata_change_proposal)
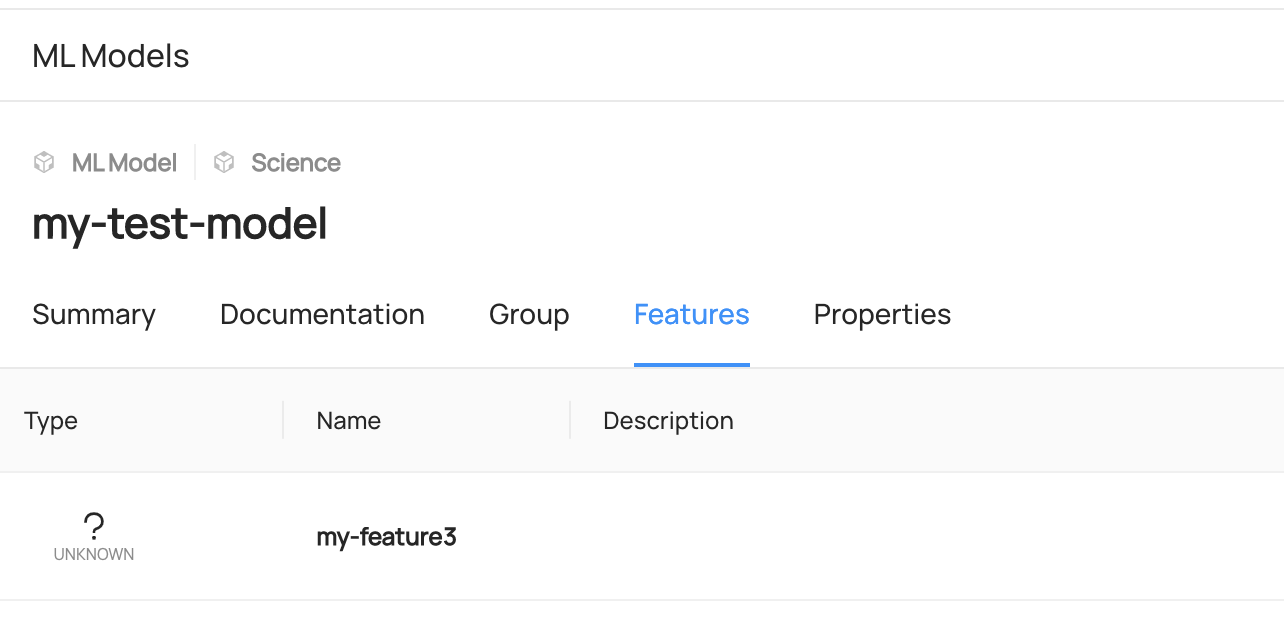
Add MlFeature to MLModel
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlfeature_add_to_mlmodel.py
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
import datahub.metadata.schema_classes as models
from datahub.emitter.mcp import MetadataChangeProposalWrapper
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
from datahub.ingestion.graph.client import DatahubClientConfig, DataHubGraph
from datahub.metadata.schema_classes import MLModelPropertiesClass
gms_endpoint = "http://localhost:8080"
# Create an emitter to DataHub over REST
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter(gms_server=gms_endpoint, extra_headers={})
model_urn = builder.make_ml_model_urn(
model_name="my-test-model", platform="science", env="PROD"
)
feature_urns = [
builder.make_ml_feature_urn(
feature_name="my-feature3", feature_table_name="my-feature-table"
),
]
# This code concatenates the new features with the existing features in the model
# If you want to replace all existing features with only the new ones, you can comment out this line.
graph = DataHubGraph(DatahubClientConfig(server=gms_endpoint))
model_properties = graph.get_aspect(
entity_urn=model_urn, aspect_type=MLModelPropertiesClass
)
if model_properties:
current_features = model_properties.mlFeatures
print("current_features:", current_features)
if current_features:
feature_urns += current_features
model_properties = models.MLModelPropertiesClass(mlFeatures=feature_urns)
# MCP creation
metadata_change_proposal = MetadataChangeProposalWrapper(
entityUrn=model_urn,
aspect=model_properties,
)
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit(metadata_change_proposal)
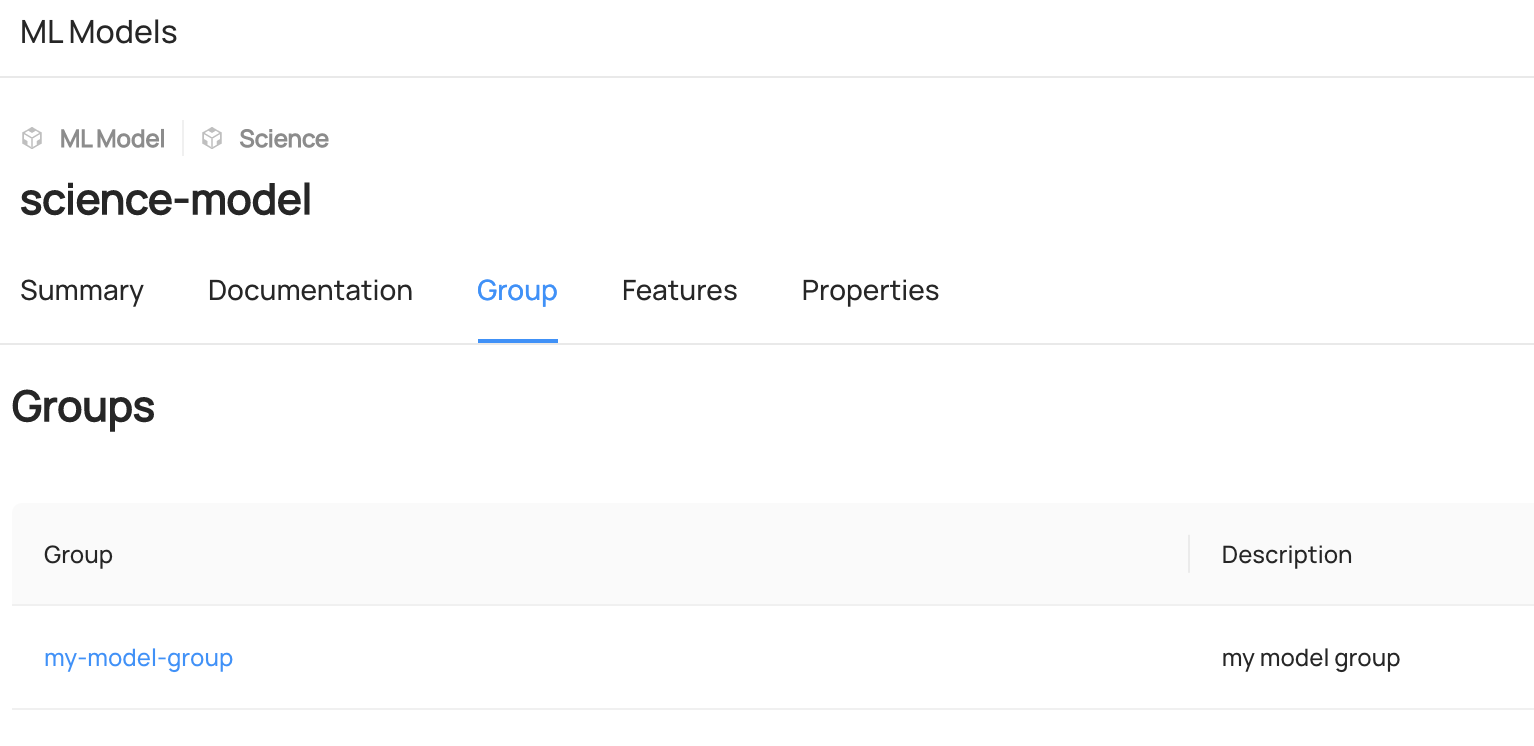
Add MLGroup To MLModel
- Python
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/mlgroup_add_to_mlmodel.py
from datahub.metadata.urns import MlModelGroupUrn
from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
from datahub.sdk.mlmodel import MLModel
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
model = MLModel(
id="my-recommendations-model",
platform="mlflow",
)
model.set_model_group(
MlModelGroupUrn(
platform="mlflow",
name="my-recommendations-model-group",
)
)
client.entities.upsert(model)
Expected Outcome of Adding ML Entities
You can access to Features or Group Tab of each entity to view the added entities.